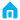
The main differences between the single and double potentiometers are reflected in the measuring principle, application scenarios, structural design and working principle.
Measurement principle: A single potentiometer can only measure one voltage and current, while a double potentiometer can measure two different voltages and currents at the same time, which is suitable for measuring the output voltage and current of a variety of circuits.
Application scenario: A single potentiometer is suitable for controlling a power supply circuit, such as a dimmer switch for a hand-held lamp. Dual potentiometers, on the other hand, are often used in circuits that need to control two power sources at the same time, such as adjusting the volume of the left and right channels of a speaker, or when the volume and pitch of the two channels in a stereo device need to be synchronized.
Structural design: The single potentiometer only needs one knob to control, and the structure is simpler and the size is smaller. The internal structure of a duplex potentiometer is more complex and requires two knobs to control, so it is usually larger in size.
Working principle: The single potentiometer does not have any contacts, so its resistance value is fixed, and it is usually used as a limiting element in the circuit. Whereas, a duplex potentiometer has two contacts, one of which is in the front and the other in the rear. When the front foot is high, the back foot is low, and the two contacts are not in contact.
Advantages and disadvantages of potentiometer single and double couplet
Potentiometer single and double potentiometers have different advantages and disadvantages, which are described below:
Single potentiometer:
Merit:
Simple structure: The single potentiometer consists of a knob and a regulator, with a relatively simple structure and compact design.
Cheap price: Due to the simple structure, the manufacturing cost of the single potentiometer is low, so the price is relatively cheap.
Small footprint: The small size of the single potentiometer makes it suitable for use in applications where space is limited.
Shortcoming:
Single function: A single potentiometer can only control the resistance value of a circuit or electrical appliance, and its function is relatively simple.
Limited Adjustment Range: Single potentiometers have a limited adjustment range and may not be able to meet the needs of some applications that require a wider range of regulation.
Duplex potentiometer:
Merit:
Versatile: The duplex potentiometer has two adjustment shafts, which can control the resistance value of two circuits or electrical appliances at the same time, and the functions are more diverse.
Space-saving: Compared to two separate single potentiometers, the dual potentiometer can reduce the footprint and make the circuit layout more compact.
Flexibility: The two knobs of the duplex potentiometer can be adjusted independently or in tandem, providing greater flexibility.
Excellent performance: Duplex potentiometers usually have the advantages of excellent heat resistance, high resolution, wide frequency range, low noise and small distributed inductance.
Shortcoming:
Complex structure: The internal structure of the duplex potentiometer is relatively complex, and the manufacturing cost is high, so the price is relatively expensive.
High requirements for adjustment accuracy: Since the double potentiometer needs to control the resistance value of two circuits or electrical appliances at the same time, the requirements for adjustment accuracy are high

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!