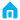
The difference between potentiometer single and duplex, the advantages and disadvantages of potentiometer single and duplex
Sure, here's the translation of the previous explanation into English:
The potentiometers, single-gang and dual-gang, differ significantly in several aspects, including measurement principles, application scenarios, structural designs, and working mechanisms. Below is a detailed elaboration of these differences, along with a discussion of their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Differences between Single-Gang and Dual-Gang Potentiometers
- Measurement Principles
- Single-Gang Potentiometer: Capable of measuring a single voltage and current, suitable for adjusting a single circuit parameter.
- Dual-Gang Potentiometer: Able to simultaneously measure two different voltages and currents, suitable for scenarios requiring the adjustment of multiple circuit parameters simultaneously.
- Application Scenarios
- Single-Gang Potentiometer: Commonly used in controlling a single power circuit, such as a dimmer switch for a handheld lamp, where only one parameter needs to be adjusted.
- Dual-Gang Potentiometer: Applicable in circuits that require the simultaneous control of two power sources, like volume and tone adjustments for both channels in a stereo audio equipment, necessitating the synchronous adjustment of two parameters.
- Structural Design
- Single-Gang Potentiometer: Relatively simple in structure, consisting of a single knob and an adjuster, making it compact and space-saving.
- Dual-Gang Potentiometer: More complex internally, requiring two knobs for control. It can be designed with coaxial shafts (where both potentiometers share the same axis) or independent shafts (where each axis adjusts its associated contact point without interference).
- Working Mechanism
- Single-Gang Potentiometer: Does not have contacts and has a fixed resistance value, often used as a limiting element in circuits.
- Dual-Gang Potentiometer: Has two contact points and allows the simultaneous adjustment of resistance values in two circuits through the rotation of knobs, enabling the synchronous adjustment of two parameters.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Single-Gang and Dual-Gang Potentiometers
Single-Gang Potentiometer
Advantages:
- Simple Structure: Consisting of a single knob and adjuster, it has a compact design.
- Cost-Effective: Lower manufacturing costs due to its simplicity, translating to a more affordable price.
- Space-Saving: Suitable for applications with limited space.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Functionality: Capable of controlling only one circuit or device's resistance value, offering limited functionality.
- Restricted Adjustment Range: May not meet the requirements of applications requiring a broader adjustment range.
Dual-Gang Potentiometer
Advantages:
- Versatile Functionality: With two adjustment shafts, it can simultaneously control the resistance values of two circuits or devices, offering increased versatility.
- Space-Efficient: Compared to two separate single-gang potentiometers, it reduces space usage, enabling a more compact circuit layout.
- Enhanced Flexibility: The two knobs can be adjusted independently or in unison, providing greater flexibility.
- Excellent Performance: Often features good heat resistance, high resolution, a wide operating frequency range, low noise, and small distributed inductance.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Structure: The internal structure is relatively complex, leading to higher manufacturing costs and a subsequently higher price.
- High Adjustment Precision Requirements: Due to the need to simultaneously control two circuits or devices' resistance values, higher adjustment precision is required.
- Potential Wear Resistance Issues: Although not universal, some dual-gang potentiometers may exhibit poor wear resistance.
In summary, single-gang and dual-gang potentiometers differ significantly in their measurement principles, application scenarios, structural designs, and working mechanisms, each with their unique advantages and disadvantages. The choice between them should be based on specific application requirements and circuit specifications.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!