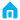
The main difference between potentiometers B103 and B502 lies in their maximum resistance values.
-
B103: Represents an adjustable potentiometer with a maximum resistance of 10KΩ (i.e., 10,000Ω). Here, "103" follows a specific notation where "10" is the significant digit and "3" indicates that three zeros need to be added after "10", resulting in 10,000.
-
B502: Indicates an adjustable potentiometer with a maximum resistance of 5KΩ (i.e., 5,000Ω). Similarly, "502" has "50" as the significant digit, and "2" means that two zeros need to be appended after "50", yielding 5,000.
In terms of appearance and usage, both may look similar, typically featuring a circular disk with a rotating axis. These types of potentiometers are commonly found in old-fashioned radios, primarily used for volume control or other applications requiring continuous adjustment of resistance values.
When selecting a potentiometer, the specific requirements of the circuit, such as the desired resistance range, must be taken into account. If the circuit necessitates a broader range of resistance adjustment, B103 may be the choice. Conversely, if a narrower range suffices, B502 could be more suitable.
Apart from resistance values, factors like power rating, accuracy, reliability, and operating environment should also be considered when selecting a potentiometer.
In summary, the key difference between potentiometers B103 and B502 lies in their maximum resistance values, with B103 being 10KΩ and B502 being 5KΩ. The appropriate model should be chosen based on the specific requirements and parameters of the circuit.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!